Dollar Cost Averaging Frequency: Daily, Weekly or Monthly?

Introduction:
Investing in the stock market can be a daunting task, especially for beginners. With so many investment strategies available, it’s crucial to find an approach that suits your financial goals and risk tolerance. One popular strategy that has gained traction over the years is dollar cost averaging. In this article, we will explore the different frequencies of dollar cost averaging, namely daily, weekly, and monthly, and discuss the factors you should consider when deciding which frequency to choose.
What is Dollar Cost Averaging?
Before delving into the various frequencies, let’s first understand what dollar cost averaging entails. Dollar cost averaging is an investment technique where an individual consistently invests a fixed amount of money at regular intervals, regardless of the share price. By doing so, investors can buy more shares when prices are low and fewer shares when prices are high, ultimately reducing the impact of short-term market fluctuations.
Choosing the Frequency of Dollar Cost Averaging:
Daily Dollar Cost Averaging:
Daily dollar cost averaging involves investing a fixed amount of money into the market on a daily basis. This frequency offers certain advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages
- Regular investment: Daily contributions allow investors to build their investment portfolio quickly.
- Capitalizing on short-term fluctuations: By investing daily, you have the opportunity to buy stocks at varying prices, taking advantage of short-term market fluctuations.
- Disciplined approach: Daily investing instills a sense of discipline and commitment towards your investment strategy.
Disadvantages
-
- Transaction costs: Daily investing may lead to higher transaction costs, as you’ll be making more frequent trades.
- Time commitment: Investing daily requires monitoring the market regularly, which can be time-consuming.
Weekly Dollar-Cost Averaging:
Weekly dollar cost averaging involves investing a fixed amount of money into the market on a weekly basis. Let’s explore the advantages and disadvantages of this frequency.
Advantages
- Reduced transaction costs: Weekly investing can help lower transaction costs compared to daily investing.
- Time management: Weekly contributions allow investors to have more time to research and analyze their investment choices.
- Smoothing out short-term volatility: Weekly contributions can help smooth out short-term market volatility.
Disadvantages
- Slower portfolio growth: Compared to daily investing, weekly contributions may result in slower portfolio growth.
- Limited exposure to short-term opportunities: Investing on a weekly basis may cause you to miss out on short-term investment opportunities.
Monthly Dollar Cost Averaging:
Monthly dollar cost averaging involves investing a fixed amount of money into the market on a monthly basis. Let’s examine the advantages and disadvantages of this frequency.
Advantages
- Lower transaction costs: Monthly investing typically incurs lower transaction costs compared to daily or weekly investing.
- Reduced time commitment: Monthly contributions require less time monitoring the market, providing investors with more flexibility.
- Long-term focus: Monthly investing encourages a long-term perspective, aligning with the principles of dollar-cost averaging.
Disadvantages
- Missed short-term opportunities: Monthly contributions may cause you to miss out on short-term market opportunities.
- Slower capital accumulation: Monthly investing may result in slower capital accumulation compared to more frequent frequencies.
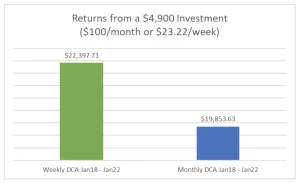
Factors to Consider:
When deciding on the frequency of your dollar cost averaging strategy, it’s important to consider the following factors:
Investment Goals
Your investment goals play a crucial role in determining the frequency of your dollar cost averaging strategy. If you have long-term goals, such as retirement planning, monthly dollar cost averaging might be a suitable option. On the other hand, if you have shorter-term goals, daily or weekly investing might align better with your objectives.
Market Volatility
The level of market volatility should also be considered. If the market is highly volatile, daily or weekly investing might help take advantage of short-term price fluctuations. Conversely, during periods of stability, monthly investing could be a more prudent choice.
Transaction Costs
Transaction costs can eat into your investment returns. If minimizing costs is a priority, opting for monthly investing might be a sensible decision. However, if you have a well-diversified portfolio and believe the benefits of more frequent investing outweigh the transaction costs, daily or weekly dollar cost averaging might be worth considering.
Choosing the Right Frequency:
Choosing the right frequency ultimately depends on your individual circumstances, investment goals, and risk tolerance. There is no one-size-fits-all approach. It’s essential to evaluate your financial situation and preferences carefully before deciding on the frequency that suits you best.
Conclusion:
Dollar cost averaging is a popular investment strategy that helps mitigate the impact of short-term market fluctuations. The frequency at which you employ this strategy, whether it’s daily, weekly, or monthly, should align with your investment goals, market volatility, and transaction costs. By carefully considering these factors, you can make an informed decision that maximizes the benefits of dollar-cost averaging while aligning with your unique circumstances.
FAQs
Q1: Is dollar cost averaging suitable for all types of investments?
Dollar cost averaging is suitable for a wide range of investments, including stocks, mutual funds, and exchange-traded funds (ETFs).
Q2: Can I change the frequency of my dollar cost averaging strategy?
Yes, you can change the frequency of your dollar-cost averaging strategy based on your changing financial goals and market conditions.
Q3: Is it better to invest in a lump sum or use dollar cost averaging?
The answer depends on your risk tolerance and market conditions. Dollar cost averaging can help reduce the impact of market volatility, but investing a lump sum can provide immediate exposure to potential gains.
Q4: How long should I continue dollar cost averaging?
Dollar cost averaging is a long-term investment strategy. It’s advisable to continue the practice until you achieve your investment goals or your circumstances change significantly.
Q5: Should I seek professional advice before implementing a dollar cost averaging strategy?
It’s always beneficial to consult with a financial advisor or investment professional who can provide personalized guidance based on your specific needs and goals.




